News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian

Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Research methods--quantitative, qualitative, and more: overview.
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Data Science Methods (Machine Learning, AI, Big Data)
- Text Mining and Computational Text Analysis
- Evidence Synthesis/Systematic Reviews
- Get Data, Get Help!
About Research Methods
This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley.
As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods , "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise. They are the "how" for building systematic knowledge. The accumulation of knowledge through research is by its nature a collective endeavor. Each well-designed study provides evidence that may support, amend, refute, or deepen the understanding of existing knowledge...Decisions are important throughout the practice of research and are designed to help researchers collect evidence that includes the full spectrum of the phenomenon under study, to maintain logical rules, and to mitigate or account for possible sources of bias. In many ways, learning research methods is learning how to see and make these decisions."
The choice of methods varies by discipline, by the kind of phenomenon being studied and the data being used to study it, by the technology available, and more. This guide is an introduction, but if you don't see what you need here, always contact your subject librarian, and/or take a look to see if there's a library research guide that will answer your question.
Suggestions for changes and additions to this guide are welcome!
START HERE: SAGE Research Methods
Without question, the most comprehensive resource available from the library is SAGE Research Methods. HERE IS THE ONLINE GUIDE to this one-stop shopping collection, and some helpful links are below:
- SAGE Research Methods
- Little Green Books (Quantitative Methods)
- Little Blue Books (Qualitative Methods)
- Dictionaries and Encyclopedias
- Case studies of real research projects
- Sample datasets for hands-on practice
- Streaming video--see methods come to life
- Methodspace- -a community for researchers
- SAGE Research Methods Course Mapping
Library Data Services at UC Berkeley
Library Data Services Program and Digital Scholarship Services
The LDSP offers a variety of services and tools ! From this link, check out pages for each of the following topics: discovering data, managing data, collecting data, GIS data, text data mining, publishing data, digital scholarship, open science, and the Research Data Management Program.
Be sure also to check out the visual guide to where to seek assistance on campus with any research question you may have!
Library GIS Services
Other Data Services at Berkeley
D-Lab Supports Berkeley faculty, staff, and graduate students with research in data intensive social science, including a wide range of training and workshop offerings Dryad Dryad is a simple self-service tool for researchers to use in publishing their datasets. It provides tools for the effective publication of and access to research data. Geospatial Innovation Facility (GIF) Provides leadership and training across a broad array of integrated mapping technologies on campu Research Data Management A UC Berkeley guide and consulting service for research data management issues
General Research Methods Resources
Here are some general resources for assistance:
- Assistance from ICPSR (must create an account to access): Getting Help with Data , and Resources for Students
- Wiley Stats Ref for background information on statistics topics
- Survey Documentation and Analysis (SDA) . Program for easy web-based analysis of survey data.
Consultants
- D-Lab/Data Science Discovery Consultants Request help with your research project from peer consultants.
- Research data (RDM) consulting Meet with RDM consultants before designing the data security, storage, and sharing aspects of your qualitative project.
- Statistics Department Consulting Services A service in which advanced graduate students, under faculty supervision, are available to consult during specified hours in the Fall and Spring semesters.
Related Resourcex
- IRB / CPHS Qualitative research projects with human subjects often require that you go through an ethics review.
- OURS (Office of Undergraduate Research and Scholarships) OURS supports undergraduates who want to embark on research projects and assistantships. In particular, check out their "Getting Started in Research" workshops
- Sponsored Projects Sponsored projects works with researchers applying for major external grants.
- Next: Quantitative Research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/researchmethods
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research analysis - latest articles
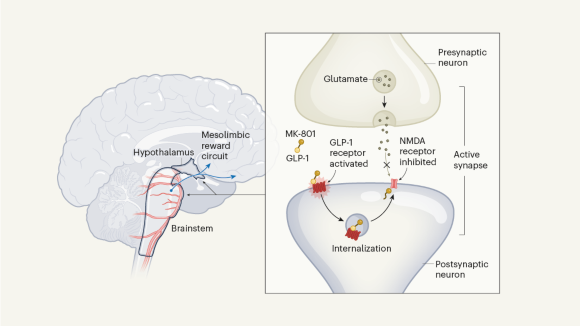
Dual-action obesity drug rewires brain circuits for appetite
A two-in-one drug that modulates neural pathways involved in appetite and reward might prove to be more effective and longer lasting than current weight-loss drugs on the market.
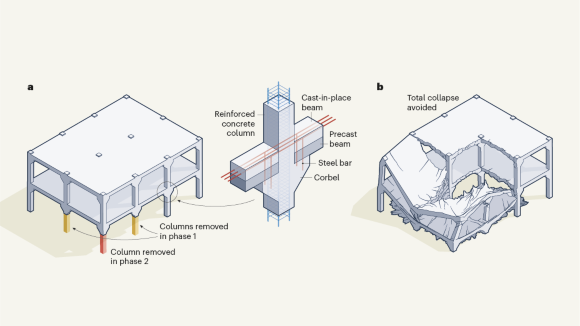
Strategic links save buildings from total collapse
A design principle for buildings incorporates components that can control the propagation of failure by isolating parts of the structure as they fail — offering a way to prevent a partial collapse snowballing into complete destruction.
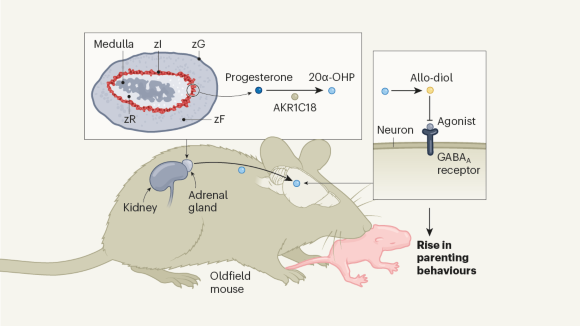
Parental-care puzzle in mice solved by thinking outside the brain
Both parents of oldfield mice care for offspring, whereas in deer mice, mothers usually care for pups. The discovery of a type of adrenal-gland cell that is present in oldfield mice but not in deer mice helps to explain the difference.
Balls of lightning and flames from the sky: can science explain?
A book cataloguing mysterious events challenges scientists to provide some answers, and Charles Darwin continues his investigations of crimes against primroses, in the weekly dip into Nature ’s archive.
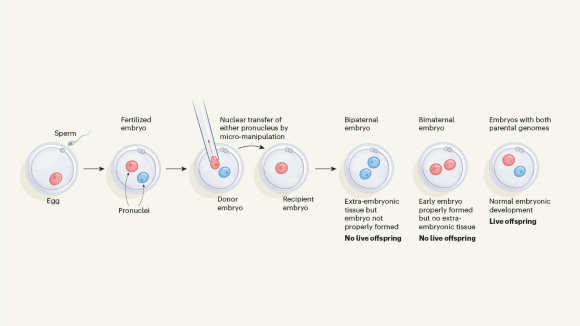
The phenomenon of genomic imprinting was discovered 40 years ago
Some genes carry an ‘imprint’ on either the maternal or the paternal copy, which determines whether or not that copy is expressed. This 1984 discovery changed how scientists think about gene regulation and inheritance.
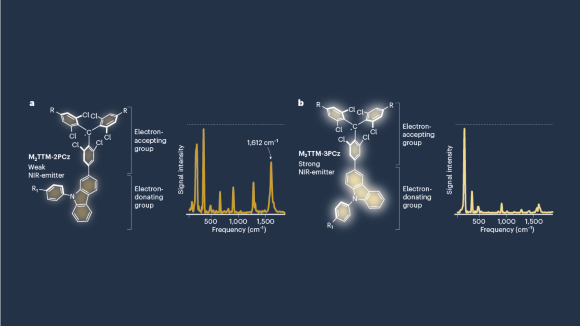
Vibration isolation could boost performance of near-infrared organic LEDs
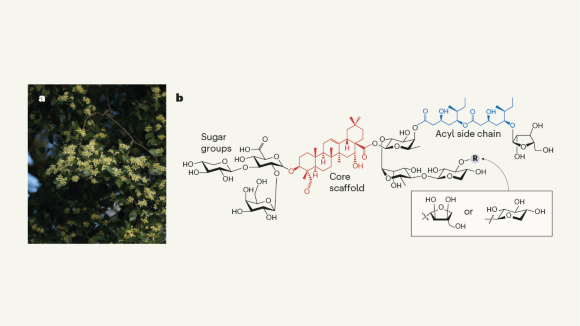
Vaccine-enhancing plant extract could be mass produced in yeast
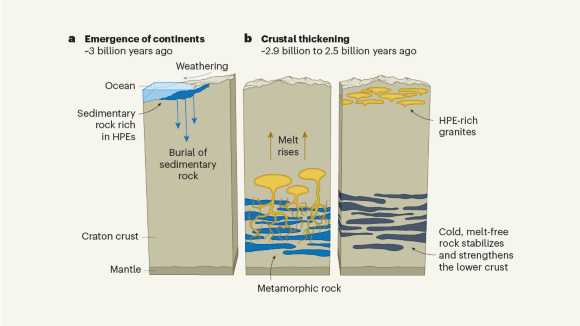
Did atmospheric weathering help Earth’s earliest continents to survive?
The dream of electronic newspapers becomes a reality — in 1974
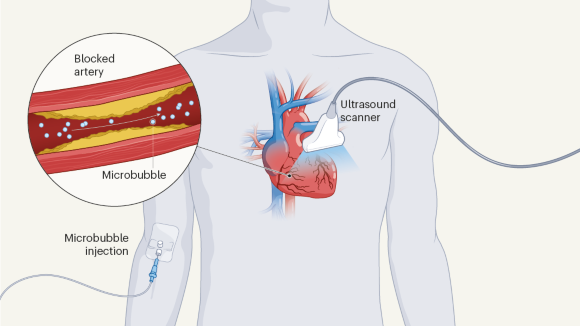
Microbubble ultrasound maps hidden signs of heart disease

Streamlined skull helps foxes take a nosedive
Advertisement
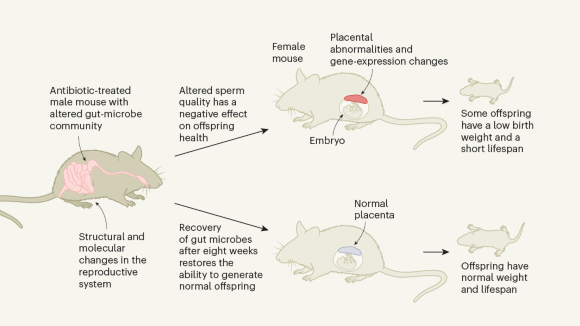
Dad’s gut microbes matter for pregnancy health and baby’s growth
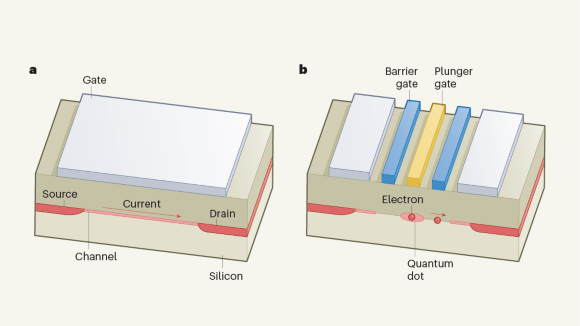
Intel brings quantum-computing microchips a step closer
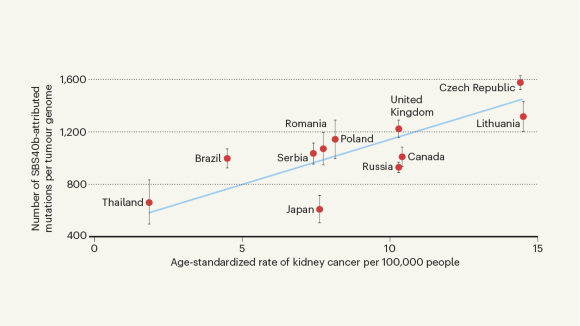
Genomics reveal unknown mutation-promoting agents at global sites
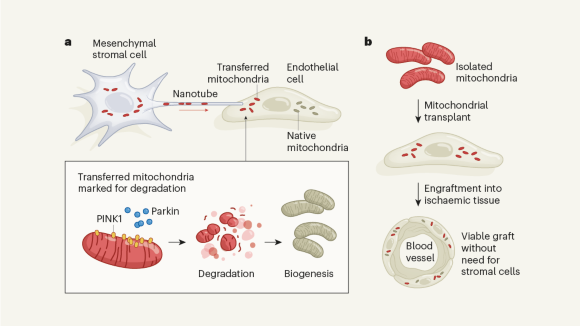
Cells destroy donated mitochondria to build blood vessels
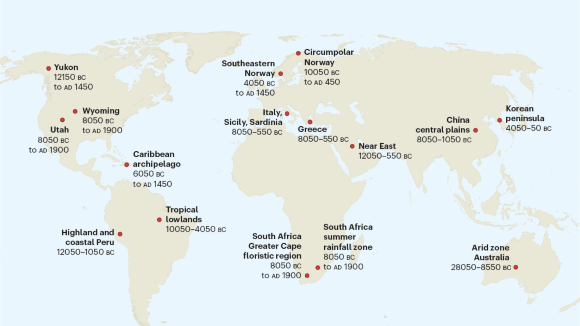
Resilience lessons from ancient societies are still relevant today
How to stop students cramming for exams? Send them to sea
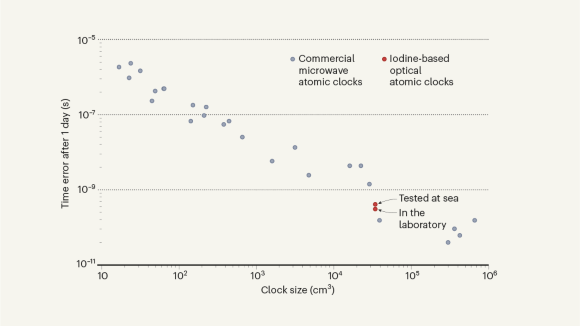
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
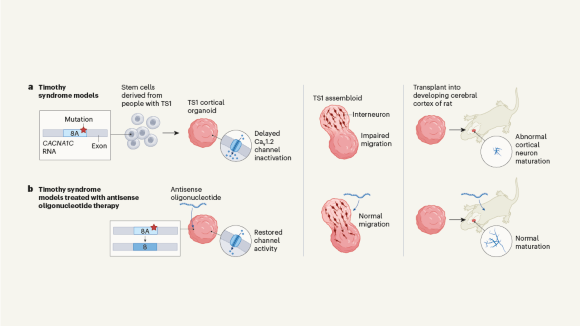
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
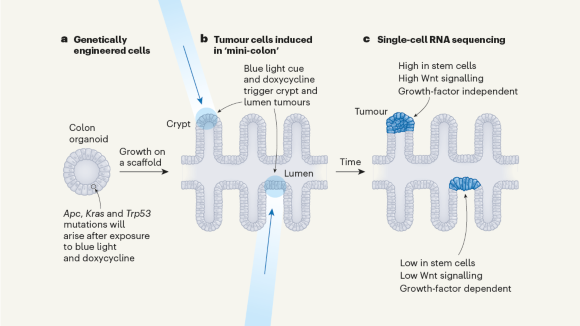
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression

Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
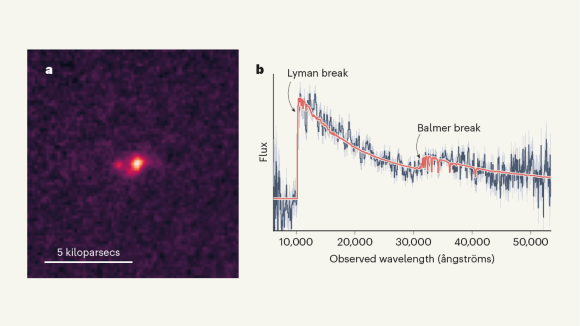
Galaxy found napping in the primordial Universe
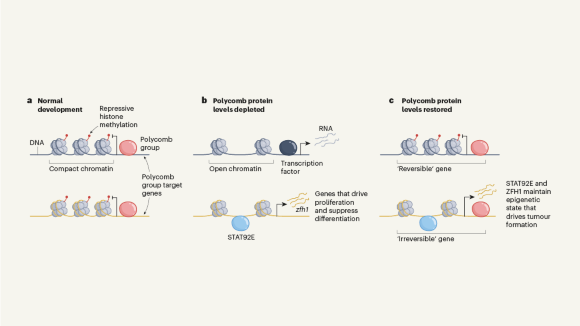
Tumours form without genetic mutations

Marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved
Charles Darwin investigates: the curious case of primrose punishment
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
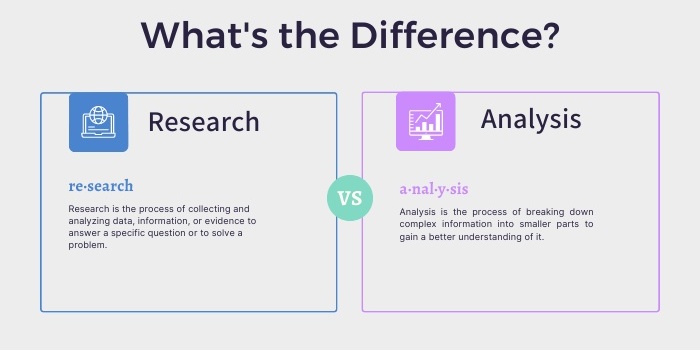
Research vs Analysis: What's the Difference and Why It Matters

When it comes to data-driven business decisions, research and analysis are often used interchangeably. However, these terms are not synonymous, and understanding the difference between them is crucial for making informed decisions.
Here are our five key takeaways:
- Research is the process of finding information, while analysis is the process of evaluating and interpreting that information to make informed decisions.
- Analysis is a critical step in the decision-making process, providing context and insights to support informed choices.
- Good research is essential to conducting effective analysis, but research alone is not enough to inform decision-making.
- Analysis requires a range of skills, including data modeling, statistics, and critical thinking.
- While analysis can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, it is a necessary step for making informed decisions based on data.
In this article, we'll explore the key differences between research and analysis and why they matter in the decision-making process.
Table of Contents
Understanding research vs analysis, why analysis matters in the decision-making process, the role of research in analysis, skills needed for effective analysis, the time and resource requirements for analysis, the unified stack for modern data teams, get a personalized platform demo & 30-minute q&a session with a solution engineer, introduction.
This is a guest post by Bill Inmon. Bill Inmon is a pioneer in data warehousing, widely known as the “Father of Data Warehousing.” He is also the author of more than 50 books and over 650 articles on data warehousing, data management, and information technology.
The search vendors will tell you that there is no difference. Indeed, when you do analysis you have to do research. But there are some very real and very important differences.
When it comes to the methodology of data science, understanding the main difference between research and analysis is crucial.
What is Research?
Research is the process of collecting and analyzing data, information, or evidence to answer a specific question or to solve a problem. It involves identifying a research question, designing a study or experiment, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions based on the results.
Research is typically focused on gathering information through various qualitative research methods, in order to develop an understanding of a particular topic or phenomenon.
In its simplest form, it means we go look for something. We go to a library and we find some books. Or we go to the Internet and find a good restaurant to go to. Or we go to the Bible and look up the story of Cain and Abel. To research means to go to a body of elements and find the one or two that we need for our purposes.
What are some common research methods?
There are many research methods, but some common ones include surveys, experiments, observational studies, case studies, and interviews. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method depends on the research question, the type of data needed, and the available resources.
What is Analysis?
Analysis is the process of breaking down complex information into smaller parts to gain a better understanding of it. Then take that information and apply statistical analysis and other methods to draw conclusions and make predictions.
Somewhat similar to research, we go to a body of elements and find one or two that are of interest to us. Then after finding what we are looking for we do further investigation.
That further investigation may take many forms.
- We may compare and contrast the elements
- We may simply count and summarize the elements
- We may look at many elements and qualify some of them and disqualify the others
The goal of analysis is to answer questions or solve problems. Analysis often involves examining and interpreting data sets, identifying patterns and trends, and drawing predictive conclusions based on the evidence.
In contrast to research, which is focused on gathering data, analysis is focused on making sense of the data that has already been collected.
What are some common analysis methods?
In the analysis process, data scientists use a variety of techniques and tools to explore and analyze the data, such as regression analysis, clustering, and machine learning algorithms. These techniques are used to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends in the data that can help inform business decisions and strategies.
There are many analysis methods, but some common ones include descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, content analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method depends on the type of data collected, the research question, and the available resources.
Analysis is a critical step in the decision-making process. It provides context and insights to support informed choices. Without analysis, decision-makers risk making choices based on incomplete or inaccurate information, leading to poor outcomes. Effective analysis helps decision-makers understand the impact of different scenarios, identify potential risks, and identify opportunities for improvement.
In almost every case, the analysis starts with quantitative research. So it’s almost like differentiating between baiting a hook and catching a fish. If you are going to catch a fish, you have to start by baiting a hook.
Although that might not be the best analogy, the role of research in analysis works in the same order. Good research is essential to conducting effective analysis. It provides a foundation of knowledge and understanding, helping analysts identify patterns, trends, and relationships in data collection. However, research alone is not enough to inform decision-making. Just like baiting a hook alone is not enough to catch a fish.
Effective analysis requires a range of skills, including data modeling, statistics, and critical thinking. Data modeling involves creating a conceptual framework for understanding the data, while statistics helps data analysts identify patterns and relationships in the data sets. Critical thinking is essential for evaluating data analytics and drawing insights that support informed decision-making.
Related Reading : The Best Data Modeling Tools: Advice & Comparison
Just because you search for something does not mean you are going to analyze it.
Analysis can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring significant investments in technology, talent, and infrastructure. However, It is necessary to analyze something when you need to extract meaningful insights or draw conclusions based on big data or information gathered through quantitative research.
Whether you're conducting research or performing statistical analysis, having a solid understanding of your data and how to interpret it is essential for success. Data scientists play a critical role in this process, as they have the skills and expertise to apply statistical methods and other techniques to make sense of complex data sets.
Organizations that invest in effective analysis capabilities are better positioned to make predictive data-driven business decisions that support their strategic goals. Without quantitative analysis, research may remain incomplete or inconclusive, and the data gathered may not be effectively used.
Related Reading : 7 Best Data Analysis Tools
How Integrate.io Can Help
When it comes to search and analysis, having access to accurate and reliable data is essential for making informed decisions. This is where Integrate.io comes in - as a big data integration platform, it enables businesses to connect and combine data from a variety of sources, making it easier to search for and analyze the information that's most relevant to their needs. By streamlining the data integration process, Integrate.io helps businesses get the most out of their data collection, enabling them to make more informed decisions and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
In conclusion, the main difference between research and analysis lies in the approach to data collection and interpretation. While research is focused on gathering information through qualitative research methods, analysis is focused on drawing predictive conclusions based on statistical analysis and other techniques. By leveraging the power of data science and tools like Integrate.io , businesses can make better decisions based on data-driven insights.
Tags: big data, data-analytics, Versus
Related Readings

Why Data Democratization Matters Today

Snowpark Unleashed: Data Magic Within Snowflake

The Essential Role of a Data Steward in Modern Business Intelligence
Subscribe to the stack newsletter.
[email protected] +1-888-884-6405
©2024 Integrate.io
- Solutions Home
- Release Notes
- Support & Resources
- Documentation
- Documentation API
- Service Status
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Consent Preferences
- White Papers
Get the Integrate.io Newsletter
Choose your free trial, etl & reverse etl, formerly xplenty.
Low-code ETL with 220+ data transformations to prepare your data for insights and reporting.
Formerly FlyData
Replicate data to your warehouses giving you real-time access to all of your critical data.
API Generation
Formerly dreamfactory.
Generate a REST API on any data source in seconds to power data products.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HCA Healthc J Med
- v.1(2); 2020
- PMC10324782

Introduction to Research Statistical Analysis: An Overview of the Basics
Christian vandever.
1 HCA Healthcare Graduate Medical Education
Description
This article covers many statistical ideas essential to research statistical analysis. Sample size is explained through the concepts of statistical significance level and power. Variable types and definitions are included to clarify necessities for how the analysis will be interpreted. Categorical and quantitative variable types are defined, as well as response and predictor variables. Statistical tests described include t-tests, ANOVA and chi-square tests. Multiple regression is also explored for both logistic and linear regression. Finally, the most common statistics produced by these methods are explored.
Introduction
Statistical analysis is necessary for any research project seeking to make quantitative conclusions. The following is a primer for research-based statistical analysis. It is intended to be a high-level overview of appropriate statistical testing, while not diving too deep into any specific methodology. Some of the information is more applicable to retrospective projects, where analysis is performed on data that has already been collected, but most of it will be suitable to any type of research. This primer will help the reader understand research results in coordination with a statistician, not to perform the actual analysis. Analysis is commonly performed using statistical programming software such as R, SAS or SPSS. These allow for analysis to be replicated while minimizing the risk for an error. Resources are listed later for those working on analysis without a statistician.
After coming up with a hypothesis for a study, including any variables to be used, one of the first steps is to think about the patient population to apply the question. Results are only relevant to the population that the underlying data represents. Since it is impractical to include everyone with a certain condition, a subset of the population of interest should be taken. This subset should be large enough to have power, which means there is enough data to deliver significant results and accurately reflect the study’s population.
The first statistics of interest are related to significance level and power, alpha and beta. Alpha (α) is the significance level and probability of a type I error, the rejection of the null hypothesis when it is true. The null hypothesis is generally that there is no difference between the groups compared. A type I error is also known as a false positive. An example would be an analysis that finds one medication statistically better than another, when in reality there is no difference in efficacy between the two. Beta (β) is the probability of a type II error, the failure to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false. A type II error is also known as a false negative. This occurs when the analysis finds there is no difference in two medications when in reality one works better than the other. Power is defined as 1-β and should be calculated prior to running any sort of statistical testing. Ideally, alpha should be as small as possible while power should be as large as possible. Power generally increases with a larger sample size, but so does cost and the effect of any bias in the study design. Additionally, as the sample size gets bigger, the chance for a statistically significant result goes up even though these results can be small differences that do not matter practically. Power calculators include the magnitude of the effect in order to combat the potential for exaggeration and only give significant results that have an actual impact. The calculators take inputs like the mean, effect size and desired power, and output the required minimum sample size for analysis. Effect size is calculated using statistical information on the variables of interest. If that information is not available, most tests have commonly used values for small, medium or large effect sizes.
When the desired patient population is decided, the next step is to define the variables previously chosen to be included. Variables come in different types that determine which statistical methods are appropriate and useful. One way variables can be split is into categorical and quantitative variables. ( Table 1 ) Categorical variables place patients into groups, such as gender, race and smoking status. Quantitative variables measure or count some quantity of interest. Common quantitative variables in research include age and weight. An important note is that there can often be a choice for whether to treat a variable as quantitative or categorical. For example, in a study looking at body mass index (BMI), BMI could be defined as a quantitative variable or as a categorical variable, with each patient’s BMI listed as a category (underweight, normal, overweight, and obese) rather than the discrete value. The decision whether a variable is quantitative or categorical will affect what conclusions can be made when interpreting results from statistical tests. Keep in mind that since quantitative variables are treated on a continuous scale it would be inappropriate to transform a variable like which medication was given into a quantitative variable with values 1, 2 and 3.
Categorical vs. Quantitative Variables
Both of these types of variables can also be split into response and predictor variables. ( Table 2 ) Predictor variables are explanatory, or independent, variables that help explain changes in a response variable. Conversely, response variables are outcome, or dependent, variables whose changes can be partially explained by the predictor variables.
Response vs. Predictor Variables
Choosing the correct statistical test depends on the types of variables defined and the question being answered. The appropriate test is determined by the variables being compared. Some common statistical tests include t-tests, ANOVA and chi-square tests.
T-tests compare whether there are differences in a quantitative variable between two values of a categorical variable. For example, a t-test could be useful to compare the length of stay for knee replacement surgery patients between those that took apixaban and those that took rivaroxaban. A t-test could examine whether there is a statistically significant difference in the length of stay between the two groups. The t-test will output a p-value, a number between zero and one, which represents the probability that the two groups could be as different as they are in the data, if they were actually the same. A value closer to zero suggests that the difference, in this case for length of stay, is more statistically significant than a number closer to one. Prior to collecting the data, set a significance level, the previously defined alpha. Alpha is typically set at 0.05, but is commonly reduced in order to limit the chance of a type I error, or false positive. Going back to the example above, if alpha is set at 0.05 and the analysis gives a p-value of 0.039, then a statistically significant difference in length of stay is observed between apixaban and rivaroxaban patients. If the analysis gives a p-value of 0.91, then there was no statistical evidence of a difference in length of stay between the two medications. Other statistical summaries or methods examine how big of a difference that might be. These other summaries are known as post-hoc analysis since they are performed after the original test to provide additional context to the results.
Analysis of variance, or ANOVA, tests can observe mean differences in a quantitative variable between values of a categorical variable, typically with three or more values to distinguish from a t-test. ANOVA could add patients given dabigatran to the previous population and evaluate whether the length of stay was significantly different across the three medications. If the p-value is lower than the designated significance level then the hypothesis that length of stay was the same across the three medications is rejected. Summaries and post-hoc tests also could be performed to look at the differences between length of stay and which individual medications may have observed statistically significant differences in length of stay from the other medications. A chi-square test examines the association between two categorical variables. An example would be to consider whether the rate of having a post-operative bleed is the same across patients provided with apixaban, rivaroxaban and dabigatran. A chi-square test can compute a p-value determining whether the bleeding rates were significantly different or not. Post-hoc tests could then give the bleeding rate for each medication, as well as a breakdown as to which specific medications may have a significantly different bleeding rate from each other.
A slightly more advanced way of examining a question can come through multiple regression. Regression allows more predictor variables to be analyzed and can act as a control when looking at associations between variables. Common control variables are age, sex and any comorbidities likely to affect the outcome variable that are not closely related to the other explanatory variables. Control variables can be especially important in reducing the effect of bias in a retrospective population. Since retrospective data was not built with the research question in mind, it is important to eliminate threats to the validity of the analysis. Testing that controls for confounding variables, such as regression, is often more valuable with retrospective data because it can ease these concerns. The two main types of regression are linear and logistic. Linear regression is used to predict differences in a quantitative, continuous response variable, such as length of stay. Logistic regression predicts differences in a dichotomous, categorical response variable, such as 90-day readmission. So whether the outcome variable is categorical or quantitative, regression can be appropriate. An example for each of these types could be found in two similar cases. For both examples define the predictor variables as age, gender and anticoagulant usage. In the first, use the predictor variables in a linear regression to evaluate their individual effects on length of stay, a quantitative variable. For the second, use the same predictor variables in a logistic regression to evaluate their individual effects on whether the patient had a 90-day readmission, a dichotomous categorical variable. Analysis can compute a p-value for each included predictor variable to determine whether they are significantly associated. The statistical tests in this article generate an associated test statistic which determines the probability the results could be acquired given that there is no association between the compared variables. These results often come with coefficients which can give the degree of the association and the degree to which one variable changes with another. Most tests, including all listed in this article, also have confidence intervals, which give a range for the correlation with a specified level of confidence. Even if these tests do not give statistically significant results, the results are still important. Not reporting statistically insignificant findings creates a bias in research. Ideas can be repeated enough times that eventually statistically significant results are reached, even though there is no true significance. In some cases with very large sample sizes, p-values will almost always be significant. In this case the effect size is critical as even the smallest, meaningless differences can be found to be statistically significant.
These variables and tests are just some things to keep in mind before, during and after the analysis process in order to make sure that the statistical reports are supporting the questions being answered. The patient population, types of variables and statistical tests are all important things to consider in the process of statistical analysis. Any results are only as useful as the process used to obtain them. This primer can be used as a reference to help ensure appropriate statistical analysis.
Funding Statement
This research was supported (in whole or in part) by HCA Healthcare and/or an HCA Healthcare affiliated entity.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares he has no conflicts of interest.
Christian Vandever is an employee of HCA Healthcare Graduate Medical Education, an organization affiliated with the journal’s publisher.
This research was supported (in whole or in part) by HCA Healthcare and/or an HCA Healthcare affiliated entity. The views expressed in this publication represent those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of HCA Healthcare or any of its affiliated entities.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types
Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types
Table of Contents

Data Analysis
Definition:
Data analysis refers to the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, drawing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to interpret and derive insights from large datasets. The ultimate aim of data analysis is to convert raw data into actionable insights that can inform business decisions, scientific research, and other endeavors.
Data Analysis Process
The following are step-by-step guides to the data analysis process:
Define the Problem
The first step in data analysis is to clearly define the problem or question that needs to be answered. This involves identifying the purpose of the analysis, the data required, and the intended outcome.
Collect the Data
The next step is to collect the relevant data from various sources. This may involve collecting data from surveys, databases, or other sources. It is important to ensure that the data collected is accurate, complete, and relevant to the problem being analyzed.
Clean and Organize the Data
Once the data has been collected, it needs to be cleaned and organized. This involves removing any errors or inconsistencies in the data, filling in missing values, and ensuring that the data is in a format that can be easily analyzed.
Analyze the Data
The next step is to analyze the data using various statistical and analytical techniques. This may involve identifying patterns in the data, conducting statistical tests, or using machine learning algorithms to identify trends and insights.
Interpret the Results
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions based on the analysis and identifying any significant findings or trends.
Communicate the Findings
Once the results have been interpreted, they need to be communicated to stakeholders. This may involve creating reports, visualizations, or presentations to effectively communicate the findings and recommendations.
Take Action
The final step in the data analysis process is to take action based on the findings. This may involve implementing new policies or procedures, making strategic decisions, or taking other actions based on the insights gained from the analysis.
Types of Data Analysis
Types of Data Analysis are as follows:
Descriptive Analysis
This type of analysis involves summarizing and describing the main characteristics of a dataset, such as the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range.
Inferential Analysis
This type of analysis involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. Inferential analysis can help determine whether a certain relationship or pattern observed in a sample is likely to be present in the entire population.

Diagnostic Analysis
This type of analysis involves identifying and diagnosing problems or issues within a dataset. Diagnostic analysis can help identify outliers, errors, missing data, or other anomalies in the dataset.
Predictive Analysis
This type of analysis involves using statistical models and algorithms to predict future outcomes or trends based on historical data. Predictive analysis can help businesses and organizations make informed decisions about the future.
Prescriptive Analysis
This type of analysis involves recommending a course of action based on the results of previous analyses. Prescriptive analysis can help organizations make data-driven decisions about how to optimize their operations, products, or services.
Exploratory Analysis
This type of analysis involves exploring the relationships and patterns within a dataset to identify new insights and trends. Exploratory analysis is often used in the early stages of research or data analysis to generate hypotheses and identify areas for further investigation.
Data Analysis Methods
Data Analysis Methods are as follows:
Statistical Analysis
This method involves the use of mathematical models and statistical tools to analyze and interpret data. It includes measures of central tendency, correlation analysis, regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and more.
Machine Learning
This method involves the use of algorithms to identify patterns and relationships in data. It includes supervised and unsupervised learning, classification, clustering, and predictive modeling.
Data Mining
This method involves using statistical and machine learning techniques to extract information and insights from large and complex datasets.
Text Analysis
This method involves using natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze and interpret text data. It includes sentiment analysis, topic modeling, and entity recognition.
Network Analysis
This method involves analyzing the relationships and connections between entities in a network, such as social networks or computer networks. It includes social network analysis and graph theory.
Time Series Analysis
This method involves analyzing data collected over time to identify patterns and trends. It includes forecasting, decomposition, and smoothing techniques.
Spatial Analysis
This method involves analyzing geographic data to identify spatial patterns and relationships. It includes spatial statistics, spatial regression, and geospatial data visualization.
Data Visualization
This method involves using graphs, charts, and other visual representations to help communicate the findings of the analysis. It includes scatter plots, bar charts, heat maps, and interactive dashboards.
Qualitative Analysis
This method involves analyzing non-numeric data such as interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses. It includes thematic analysis, content analysis, and grounded theory.
Multi-criteria Decision Analysis
This method involves analyzing multiple criteria and objectives to support decision-making. It includes techniques such as the analytical hierarchy process, TOPSIS, and ELECTRE.
Data Analysis Tools
There are various data analysis tools available that can help with different aspects of data analysis. Below is a list of some commonly used data analysis tools:
- Microsoft Excel: A widely used spreadsheet program that allows for data organization, analysis, and visualization.
- SQL : A programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases.
- R : An open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics.
- Python : A general-purpose programming language that is widely used in data analysis and machine learning.
- Tableau : A data visualization software that allows for interactive and dynamic visualizations of data.
- SAS : A statistical analysis software used for data management, analysis, and reporting.
- SPSS : A statistical analysis software used for data analysis, reporting, and modeling.
- Matlab : A numerical computing software that is widely used in scientific research and engineering.
- RapidMiner : A data science platform that offers a wide range of data analysis and machine learning tools.
Applications of Data Analysis
Data analysis has numerous applications across various fields. Below are some examples of how data analysis is used in different fields:
- Business : Data analysis is used to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and financial performance. This includes customer segmentation, sales forecasting, and market research.
- Healthcare : Data analysis is used to identify patterns and trends in patient data, improve patient outcomes, and optimize healthcare operations. This includes clinical decision support, disease surveillance, and healthcare cost analysis.
- Education : Data analysis is used to measure student performance, evaluate teaching effectiveness, and improve educational programs. This includes assessment analytics, learning analytics, and program evaluation.
- Finance : Data analysis is used to monitor and evaluate financial performance, identify risks, and make investment decisions. This includes risk management, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection.
- Government : Data analysis is used to inform policy-making, improve public services, and enhance public safety. This includes crime analysis, disaster response planning, and social welfare program evaluation.
- Sports : Data analysis is used to gain insights into athlete performance, improve team strategy, and enhance fan engagement. This includes player evaluation, scouting analysis, and game strategy optimization.
- Marketing : Data analysis is used to measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, understand customer behavior, and develop targeted marketing strategies. This includes customer segmentation, marketing attribution analysis, and social media analytics.
- Environmental science : Data analysis is used to monitor and evaluate environmental conditions, assess the impact of human activities on the environment, and develop environmental policies. This includes climate modeling, ecological forecasting, and pollution monitoring.
When to Use Data Analysis
Data analysis is useful when you need to extract meaningful insights and information from large and complex datasets. It is a crucial step in the decision-making process, as it helps you understand the underlying patterns and relationships within the data, and identify potential areas for improvement or opportunities for growth.
Here are some specific scenarios where data analysis can be particularly helpful:
- Problem-solving : When you encounter a problem or challenge, data analysis can help you identify the root cause and develop effective solutions.
- Optimization : Data analysis can help you optimize processes, products, or services to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
- Prediction: Data analysis can help you make predictions about future trends or outcomes, which can inform strategic planning and decision-making.
- Performance evaluation : Data analysis can help you evaluate the performance of a process, product, or service to identify areas for improvement and potential opportunities for growth.
- Risk assessment : Data analysis can help you assess and mitigate risks, whether it is financial, operational, or related to safety.
- Market research : Data analysis can help you understand customer behavior and preferences, identify market trends, and develop effective marketing strategies.
- Quality control: Data analysis can help you ensure product quality and customer satisfaction by identifying and addressing quality issues.
Purpose of Data Analysis
The primary purposes of data analysis can be summarized as follows:
- To gain insights: Data analysis allows you to identify patterns and trends in data, which can provide valuable insights into the underlying factors that influence a particular phenomenon or process.
- To inform decision-making: Data analysis can help you make informed decisions based on the information that is available. By analyzing data, you can identify potential risks, opportunities, and solutions to problems.
- To improve performance: Data analysis can help you optimize processes, products, or services by identifying areas for improvement and potential opportunities for growth.
- To measure progress: Data analysis can help you measure progress towards a specific goal or objective, allowing you to track performance over time and adjust your strategies accordingly.
- To identify new opportunities: Data analysis can help you identify new opportunities for growth and innovation by identifying patterns and trends that may not have been visible before.
Examples of Data Analysis
Some Examples of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Social Media Monitoring: Companies use data analysis to monitor social media activity in real-time to understand their brand reputation, identify potential customer issues, and track competitors. By analyzing social media data, businesses can make informed decisions on product development, marketing strategies, and customer service.
- Financial Trading: Financial traders use data analysis to make real-time decisions about buying and selling stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. By analyzing real-time market data, traders can identify trends and patterns that help them make informed investment decisions.
- Traffic Monitoring : Cities use data analysis to monitor traffic patterns and make real-time decisions about traffic management. By analyzing data from traffic cameras, sensors, and other sources, cities can identify congestion hotspots and make changes to improve traffic flow.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Healthcare providers use data analysis to monitor patient health in real-time. By analyzing data from wearable devices, electronic health records, and other sources, healthcare providers can identify potential health issues and provide timely interventions.
- Online Advertising: Online advertisers use data analysis to make real-time decisions about advertising campaigns. By analyzing data on user behavior and ad performance, advertisers can make adjustments to their campaigns to improve their effectiveness.
- Sports Analysis : Sports teams use data analysis to make real-time decisions about strategy and player performance. By analyzing data on player movement, ball position, and other variables, coaches can make informed decisions about substitutions, game strategy, and training regimens.
- Energy Management : Energy companies use data analysis to monitor energy consumption in real-time. By analyzing data on energy usage patterns, companies can identify opportunities to reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
Characteristics of Data Analysis
Characteristics of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Objective : Data analysis should be objective and based on empirical evidence, rather than subjective assumptions or opinions.
- Systematic : Data analysis should follow a systematic approach, using established methods and procedures for collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data.
- Accurate : Data analysis should produce accurate results, free from errors and bias. Data should be validated and verified to ensure its quality.
- Relevant : Data analysis should be relevant to the research question or problem being addressed. It should focus on the data that is most useful for answering the research question or solving the problem.
- Comprehensive : Data analysis should be comprehensive and consider all relevant factors that may affect the research question or problem.
- Timely : Data analysis should be conducted in a timely manner, so that the results are available when they are needed.
- Reproducible : Data analysis should be reproducible, meaning that other researchers should be able to replicate the analysis using the same data and methods.
- Communicable : Data analysis should be communicated clearly and effectively to stakeholders and other interested parties. The results should be presented in a way that is understandable and useful for decision-making.
Advantages of Data Analysis
Advantages of Data Analysis are as follows:
- Better decision-making: Data analysis helps in making informed decisions based on facts and evidence, rather than intuition or guesswork.
- Improved efficiency: Data analysis can identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in business processes, allowing organizations to optimize their operations and reduce costs.
- Increased accuracy: Data analysis helps to reduce errors and bias, providing more accurate and reliable information.
- Better customer service: Data analysis can help organizations understand their customers better, allowing them to provide better customer service and improve customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: Data analysis can provide organizations with insights into their competitors, allowing them to identify areas where they can gain a competitive advantage.
- Identification of trends and patterns : Data analysis can identify trends and patterns in data that may not be immediately apparent, helping organizations to make predictions and plan for the future.
- Improved risk management : Data analysis can help organizations identify potential risks and take proactive steps to mitigate them.
- Innovation: Data analysis can inspire innovation and new ideas by revealing new opportunities or previously unknown correlations in data.
Limitations of Data Analysis
- Data quality: The quality of data can impact the accuracy and reliability of analysis results. If data is incomplete, inconsistent, or outdated, the analysis may not provide meaningful insights.
- Limited scope: Data analysis is limited by the scope of the data available. If data is incomplete or does not capture all relevant factors, the analysis may not provide a complete picture.
- Human error : Data analysis is often conducted by humans, and errors can occur in data collection, cleaning, and analysis.
- Cost : Data analysis can be expensive, requiring specialized tools, software, and expertise.
- Time-consuming : Data analysis can be time-consuming, especially when working with large datasets or conducting complex analyses.
- Overreliance on data: Data analysis should be complemented with human intuition and expertise. Overreliance on data can lead to a lack of creativity and innovation.
- Privacy concerns: Data analysis can raise privacy concerns if personal or sensitive information is used without proper consent or security measures.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Cluster Analysis – Types, Methods and Examples

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Discriminant Analysis – Methods, Types and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Data Analysis in Research: Types & Methods
Content Index
Why analyze data in research?
Types of data in research, finding patterns in the qualitative data, methods used for data analysis in qualitative research, preparing data for analysis, methods used for data analysis in quantitative research, considerations in research data analysis, what is data analysis in research.
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense.
Three essential things occur during the data analysis process — the first is data organization . Summarization and categorization together contribute to becoming the second known method used for data reduction. It helps find patterns and themes in the data for easy identification and linking. The third and last way is data analysis – researchers do it in both top-down and bottom-up fashion.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
On the other hand, Marshall and Rossman describe data analysis as a messy, ambiguous, and time-consuming but creative and fascinating process through which a mass of collected data is brought to order, structure and meaning.
We can say that “the data analysis and data interpretation is a process representing the application of deductive and inductive logic to the research and data analysis.”
Researchers rely heavily on data as they have a story to tell or research problems to solve. It starts with a question, and data is nothing but an answer to that question. But, what if there is no question to ask? Well! It is possible to explore data even without a problem – we call it ‘Data Mining’, which often reveals some interesting patterns within the data that are worth exploring.
Irrelevant to the type of data researchers explore, their mission and audiences’ vision guide them to find the patterns to shape the story they want to tell. One of the essential things expected from researchers while analyzing data is to stay open and remain unbiased toward unexpected patterns, expressions, and results. Remember, sometimes, data analysis tells the most unforeseen yet exciting stories that were not expected when initiating data analysis. Therefore, rely on the data you have at hand and enjoy the journey of exploratory research.
Create a Free Account
Every kind of data has a rare quality of describing things after assigning a specific value to it. For analysis, you need to organize these values, processed and presented in a given context, to make it useful. Data can be in different forms; here are the primary data types.
- Qualitative data: When the data presented has words and descriptions, then we call it qualitative data . Although you can observe this data, it is subjective and harder to analyze data in research, especially for comparison. Example: Quality data represents everything describing taste, experience, texture, or an opinion that is considered quality data. This type of data is usually collected through focus groups, personal qualitative interviews , qualitative observation or using open-ended questions in surveys.
- Quantitative data: Any data expressed in numbers of numerical figures are called quantitative data . This type of data can be distinguished into categories, grouped, measured, calculated, or ranked. Example: questions such as age, rank, cost, length, weight, scores, etc. everything comes under this type of data. You can present such data in graphical format, charts, or apply statistical analysis methods to this data. The (Outcomes Measurement Systems) OMS questionnaires in surveys are a significant source of collecting numeric data.
- Categorical data: It is data presented in groups. However, an item included in the categorical data cannot belong to more than one group. Example: A person responding to a survey by telling his living style, marital status, smoking habit, or drinking habit comes under the categorical data. A chi-square test is a standard method used to analyze this data.
Learn More : Examples of Qualitative Data in Education
Data analysis in qualitative research
Data analysis and qualitative data research work a little differently from the numerical data as the quality data is made up of words, descriptions, images, objects, and sometimes symbols. Getting insight from such complicated information is a complicated process. Hence it is typically used for exploratory research and data analysis .
Although there are several ways to find patterns in the textual information, a word-based method is the most relied and widely used global technique for research and data analysis. Notably, the data analysis process in qualitative research is manual. Here the researchers usually read the available data and find repetitive or commonly used words.
For example, while studying data collected from African countries to understand the most pressing issues people face, researchers might find “food” and “hunger” are the most commonly used words and will highlight them for further analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis
The keyword context is another widely used word-based technique. In this method, the researcher tries to understand the concept by analyzing the context in which the participants use a particular keyword.
For example , researchers conducting research and data analysis for studying the concept of ‘diabetes’ amongst respondents might analyze the context of when and how the respondent has used or referred to the word ‘diabetes.’
The scrutiny-based technique is also one of the highly recommended text analysis methods used to identify a quality data pattern. Compare and contrast is the widely used method under this technique to differentiate how a specific text is similar or different from each other.
For example: To find out the “importance of resident doctor in a company,” the collected data is divided into people who think it is necessary to hire a resident doctor and those who think it is unnecessary. Compare and contrast is the best method that can be used to analyze the polls having single-answer questions types .
Metaphors can be used to reduce the data pile and find patterns in it so that it becomes easier to connect data with theory.
Variable Partitioning is another technique used to split variables so that researchers can find more coherent descriptions and explanations from the enormous data.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
There are several techniques to analyze the data in qualitative research, but here are some commonly used methods,
- Content Analysis: It is widely accepted and the most frequently employed technique for data analysis in research methodology. It can be used to analyze the documented information from text, images, and sometimes from the physical items. It depends on the research questions to predict when and where to use this method.
- Narrative Analysis: This method is used to analyze content gathered from various sources such as personal interviews, field observation, and surveys . The majority of times, stories, or opinions shared by people are focused on finding answers to the research questions.
- Discourse Analysis: Similar to narrative analysis, discourse analysis is used to analyze the interactions with people. Nevertheless, this particular method considers the social context under which or within which the communication between the researcher and respondent takes place. In addition to that, discourse analysis also focuses on the lifestyle and day-to-day environment while deriving any conclusion.
- Grounded Theory: When you want to explain why a particular phenomenon happened, then using grounded theory for analyzing quality data is the best resort. Grounded theory is applied to study data about the host of similar cases occurring in different settings. When researchers are using this method, they might alter explanations or produce new ones until they arrive at some conclusion.
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Data analysis in quantitative research
The first stage in research and data analysis is to make it for the analysis so that the nominal data can be converted into something meaningful. Data preparation consists of the below phases.
Phase I: Data Validation
Data validation is done to understand if the collected data sample is per the pre-set standards, or it is a biased data sample again divided into four different stages
- Fraud: To ensure an actual human being records each response to the survey or the questionnaire
- Screening: To make sure each participant or respondent is selected or chosen in compliance with the research criteria
- Procedure: To ensure ethical standards were maintained while collecting the data sample
- Completeness: To ensure that the respondent has answered all the questions in an online survey. Else, the interviewer had asked all the questions devised in the questionnaire.
Phase II: Data Editing
More often, an extensive research data sample comes loaded with errors. Respondents sometimes fill in some fields incorrectly or sometimes skip them accidentally. Data editing is a process wherein the researchers have to confirm that the provided data is free of such errors. They need to conduct necessary checks and outlier checks to edit the raw edit and make it ready for analysis.
Phase III: Data Coding
Out of all three, this is the most critical phase of data preparation associated with grouping and assigning values to the survey responses . If a survey is completed with a 1000 sample size, the researcher will create an age bracket to distinguish the respondents based on their age. Thus, it becomes easier to analyze small data buckets rather than deal with the massive data pile.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
After the data is prepared for analysis, researchers are open to using different research and data analysis methods to derive meaningful insights. For sure, statistical analysis plans are the most favored to analyze numerical data. In statistical analysis, distinguishing between categorical data and numerical data is essential, as categorical data involves distinct categories or labels, while numerical data consists of measurable quantities. The method is again classified into two groups. First, ‘Descriptive Statistics’ used to describe data. Second, ‘Inferential statistics’ that helps in comparing the data .
Descriptive statistics
This method is used to describe the basic features of versatile types of data in research. It presents the data in such a meaningful way that pattern in the data starts making sense. Nevertheless, the descriptive analysis does not go beyond making conclusions. The conclusions are again based on the hypothesis researchers have formulated so far. Here are a few major types of descriptive analysis methods.
Measures of Frequency
- Count, Percent, Frequency
- It is used to denote home often a particular event occurs.
- Researchers use it when they want to showcase how often a response is given.
Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean, Median, Mode
- The method is widely used to demonstrate distribution by various points.
- Researchers use this method when they want to showcase the most commonly or averagely indicated response.
Measures of Dispersion or Variation
- Range, Variance, Standard deviation
- Here the field equals high/low points.
- Variance standard deviation = difference between the observed score and mean
- It is used to identify the spread of scores by stating intervals.
- Researchers use this method to showcase data spread out. It helps them identify the depth until which the data is spread out that it directly affects the mean.
Measures of Position
- Percentile ranks, Quartile ranks
- It relies on standardized scores helping researchers to identify the relationship between different scores.
- It is often used when researchers want to compare scores with the average count.
For quantitative research use of descriptive analysis often give absolute numbers, but the in-depth analysis is never sufficient to demonstrate the rationale behind those numbers. Nevertheless, it is necessary to think of the best method for research and data analysis suiting your survey questionnaire and what story researchers want to tell. For example, the mean is the best way to demonstrate the students’ average scores in schools. It is better to rely on the descriptive statistics when the researchers intend to keep the research or outcome limited to the provided sample without generalizing it. For example, when you want to compare average voting done in two different cities, differential statistics are enough.
Descriptive analysis is also called a ‘univariate analysis’ since it is commonly used to analyze a single variable.
Inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make predictions about a larger population after research and data analysis of the representing population’s collected sample. For example, you can ask some odd 100 audiences at a movie theater if they like the movie they are watching. Researchers then use inferential statistics on the collected sample to reason that about 80-90% of people like the movie.
Here are two significant areas of inferential statistics.
- Estimating parameters: It takes statistics from the sample research data and demonstrates something about the population parameter.
- Hypothesis test: I t’s about sampling research data to answer the survey research questions. For example, researchers might be interested to understand if the new shade of lipstick recently launched is good or not, or if the multivitamin capsules help children to perform better at games.
These are sophisticated analysis methods used to showcase the relationship between different variables instead of describing a single variable. It is often used when researchers want something beyond absolute numbers to understand the relationship between variables.
Here are some of the commonly used methods for data analysis in research.
- Correlation: When researchers are not conducting experimental research or quasi-experimental research wherein the researchers are interested to understand the relationship between two or more variables, they opt for correlational research methods.
- Cross-tabulation: Also called contingency tables, cross-tabulation is used to analyze the relationship between multiple variables. Suppose provided data has age and gender categories presented in rows and columns. A two-dimensional cross-tabulation helps for seamless data analysis and research by showing the number of males and females in each age category.
- Regression analysis: For understanding the strong relationship between two variables, researchers do not look beyond the primary and commonly used regression analysis method, which is also a type of predictive analysis used. In this method, you have an essential factor called the dependent variable. You also have multiple independent variables in regression analysis. You undertake efforts to find out the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable. The values of both independent and dependent variables are assumed as being ascertained in an error-free random manner.
- Frequency tables: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Analysis of variance: The statistical procedure is used for testing the degree to which two or more vary or differ in an experiment. A considerable degree of variation means research findings were significant. In many contexts, ANOVA testing and variance analysis are similar.
- Researchers must have the necessary research skills to analyze and manipulation the data , Getting trained to demonstrate a high standard of research practice. Ideally, researchers must possess more than a basic understanding of the rationale of selecting one statistical method over the other to obtain better data insights.
- Usually, research and data analytics projects differ by scientific discipline; therefore, getting statistical advice at the beginning of analysis helps design a survey questionnaire, select data collection methods , and choose samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- The primary aim of data research and analysis is to derive ultimate insights that are unbiased. Any mistake in or keeping a biased mind to collect data, selecting an analysis method, or choosing audience sample il to draw a biased inference.
- Irrelevant to the sophistication used in research data and analysis is enough to rectify the poorly defined objective outcome measurements. It does not matter if the design is at fault or intentions are not clear, but lack of clarity might mislead readers, so avoid the practice.
- The motive behind data analysis in research is to present accurate and reliable data. As far as possible, avoid statistical errors, and find a way to deal with everyday challenges like outliers, missing data, data altering, data mining , or developing graphical representation.
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research The sheer amount of data generated daily is frightening. Especially when data analysis has taken center stage. in 2018. In last year, the total data supply amounted to 2.8 trillion gigabytes. Hence, it is clear that the enterprises willing to survive in the hypercompetitive world must possess an excellent capability to analyze complex research data, derive actionable insights, and adapt to the new market needs.
LEARN ABOUT: Average Order Value
QuestionPro is an online survey platform that empowers organizations in data analysis and research and provides them a medium to collect data by creating appealing surveys.
MORE LIKE THIS
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024

Pricing Analytics Software: Optimize Your Pricing Strategy
May 13, 2024

Relationship Marketing: What It Is, Examples & Top 7 Benefits
May 8, 2024

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Research Methods In Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.

Hypotheses are statements about the prediction of the results, that can be verified or disproved by some investigation.
There are four types of hypotheses :
- Null Hypotheses (H0 ) – these predict that no difference will be found in the results between the conditions. Typically these are written ‘There will be no difference…’
- Alternative Hypotheses (Ha or H1) – these predict that there will be a significant difference in the results between the two conditions. This is also known as the experimental hypothesis.
- One-tailed (directional) hypotheses – these state the specific direction the researcher expects the results to move in, e.g. higher, lower, more, less. In a correlation study, the predicted direction of the correlation can be either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (non-directional) hypotheses – these state that a difference will be found between the conditions of the independent variable but does not state the direction of a difference or relationship. Typically these are always written ‘There will be a difference ….’
All research has an alternative hypothesis (either a one-tailed or two-tailed) and a corresponding null hypothesis.
Once the research is conducted and results are found, psychologists must accept one hypothesis and reject the other.
So, if a difference is found, the Psychologist would accept the alternative hypothesis and reject the null. The opposite applies if no difference is found.
Sampling techniques
Sampling is the process of selecting a representative group from the population under study.
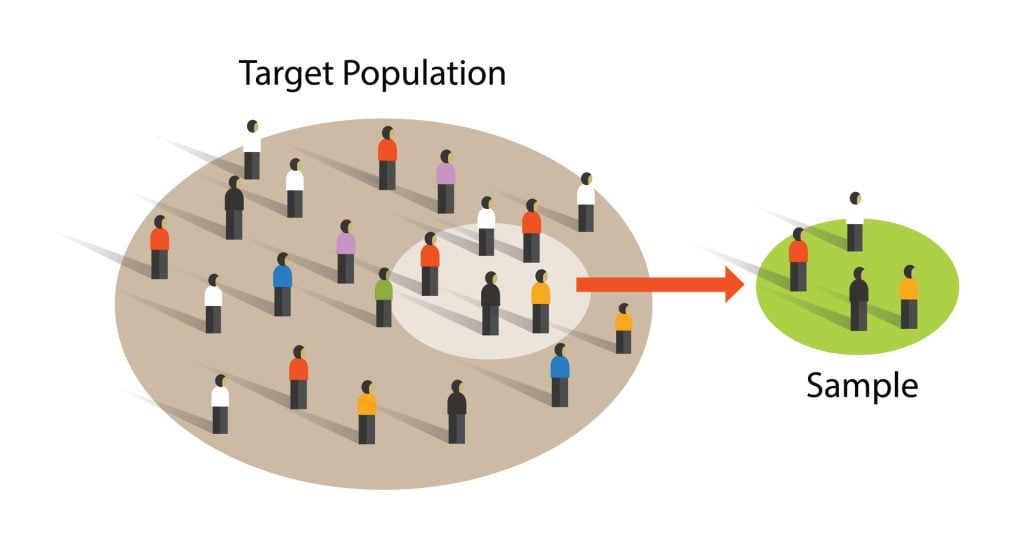
A sample is the participants you select from a target population (the group you are interested in) to make generalizations about.
Representative means the extent to which a sample mirrors a researcher’s target population and reflects its characteristics.
Generalisability means the extent to which their findings can be applied to the larger population of which their sample was a part.
- Volunteer sample : where participants pick themselves through newspaper adverts, noticeboards or online.
- Opportunity sampling : also known as convenience sampling , uses people who are available at the time the study is carried out and willing to take part. It is based on convenience.
- Random sampling : when every person in the target population has an equal chance of being selected. An example of random sampling would be picking names out of a hat.
- Systematic sampling : when a system is used to select participants. Picking every Nth person from all possible participants. N = the number of people in the research population / the number of people needed for the sample.
- Stratified sampling : when you identify the subgroups and select participants in proportion to their occurrences.
- Snowball sampling : when researchers find a few participants, and then ask them to find participants themselves and so on.
- Quota sampling : when researchers will be told to ensure the sample fits certain quotas, for example they might be told to find 90 participants, with 30 of them being unemployed.
Experiments always have an independent and dependent variable .
- The independent variable is the one the experimenter manipulates (the thing that changes between the conditions the participants are placed into). It is assumed to have a direct effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the thing being measured, or the results of the experiment.
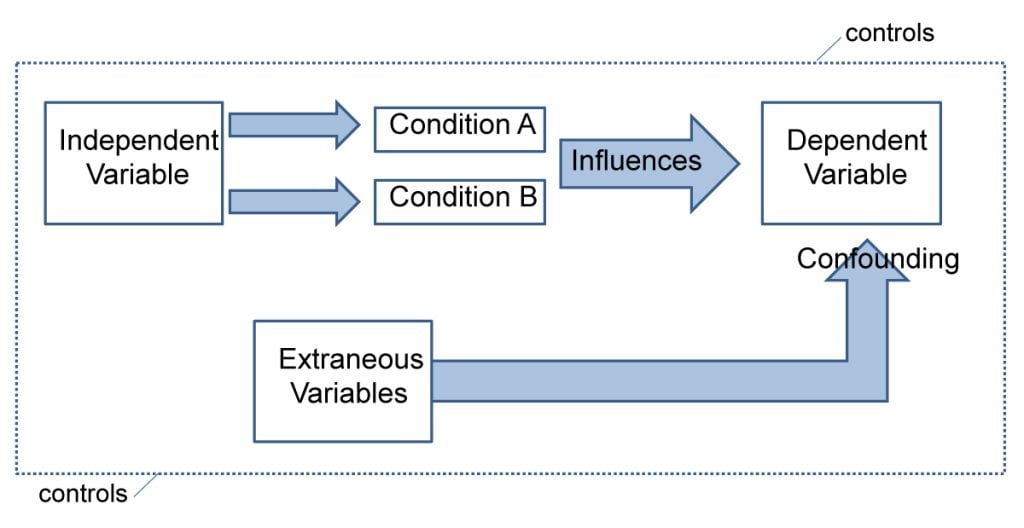
Operationalization of variables means making them measurable/quantifiable. We must use operationalization to ensure that variables are in a form that can be easily tested.
For instance, we can’t really measure ‘happiness’, but we can measure how many times a person smiles within a two-hour period.
By operationalizing variables, we make it easy for someone else to replicate our research. Remember, this is important because we can check if our findings are reliable.
Extraneous variables are all variables which are not independent variable but could affect the results of the experiment.
It can be a natural characteristic of the participant, such as intelligence levels, gender, or age for example, or it could be a situational feature of the environment such as lighting or noise.
Demand characteristics are a type of extraneous variable that occurs if the participants work out the aims of the research study, they may begin to behave in a certain way.
For example, in Milgram’s research , critics argued that participants worked out that the shocks were not real and they administered them as they thought this was what was required of them.
Extraneous variables must be controlled so that they do not affect (confound) the results.
Randomly allocating participants to their conditions or using a matched pairs experimental design can help to reduce participant variables.
Situational variables are controlled by using standardized procedures, ensuring every participant in a given condition is treated in the same way
Experimental Design
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to each condition of the independent variable, such as a control or experimental group.
- Independent design ( between-groups design ): each participant is selected for only one group. With the independent design, the most common way of deciding which participants go into which group is by means of randomization.
- Matched participants design : each participant is selected for only one group, but the participants in the two groups are matched for some relevant factor or factors (e.g. ability; sex; age).
- Repeated measures design ( within groups) : each participant appears in both groups, so that there are exactly the same participants in each group.
- The main problem with the repeated measures design is that there may well be order effects. Their experiences during the experiment may change the participants in various ways.
- They may perform better when they appear in the second group because they have gained useful information about the experiment or about the task. On the other hand, they may perform less well on the second occasion because of tiredness or boredom.
- Counterbalancing is the best way of preventing order effects from disrupting the findings of an experiment, and involves ensuring that each condition is equally likely to be used first and second by the participants.
If we wish to compare two groups with respect to a given independent variable, it is essential to make sure that the two groups do not differ in any other important way.
Experimental Methods
All experimental methods involve an iv (independent variable) and dv (dependent variable)..
- Field experiments are conducted in the everyday (natural) environment of the participants. The experimenter still manipulates the IV, but in a real-life setting. It may be possible to control extraneous variables, though such control is more difficult than in a lab experiment.
- Natural experiments are when a naturally occurring IV is investigated that isn’t deliberately manipulated, it exists anyway. Participants are not randomly allocated, and the natural event may only occur rarely.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. It uses information from a range of sources, such as from the person concerned and also from their family and friends.
Many techniques may be used such as interviews, psychological tests, observations and experiments. Case studies are generally longitudinal: in other words, they follow the individual or group over an extended period of time.
Case studies are widely used in psychology and among the best-known ones carried out were by Sigmund Freud . He conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
Case studies provide rich qualitative data and have high levels of ecological validity. However, it is difficult to generalize from individual cases as each one has unique characteristics.
Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it is a measure of the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable.
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants, and then assessing the degree of association between the measures.
The predictor variable can be seen as occurring before the outcome variable in some sense. It is called the predictor variable, because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable.
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient.
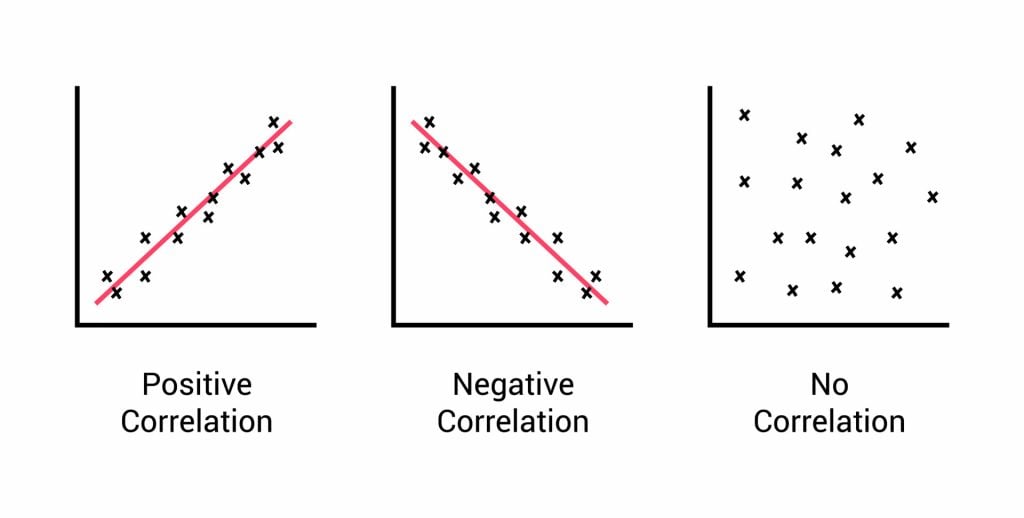
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation .
- If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation .
- A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables.
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho.
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient . This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63.
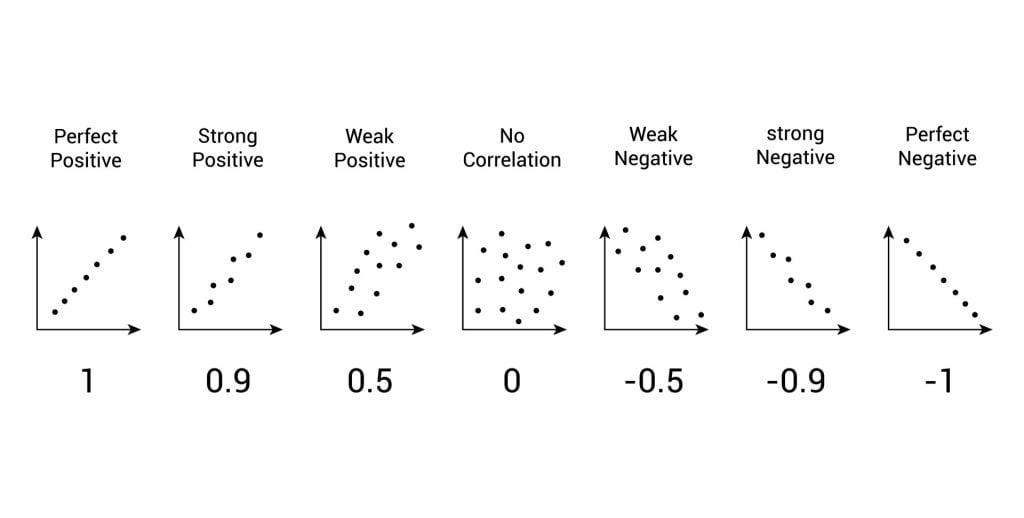
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables.
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved.
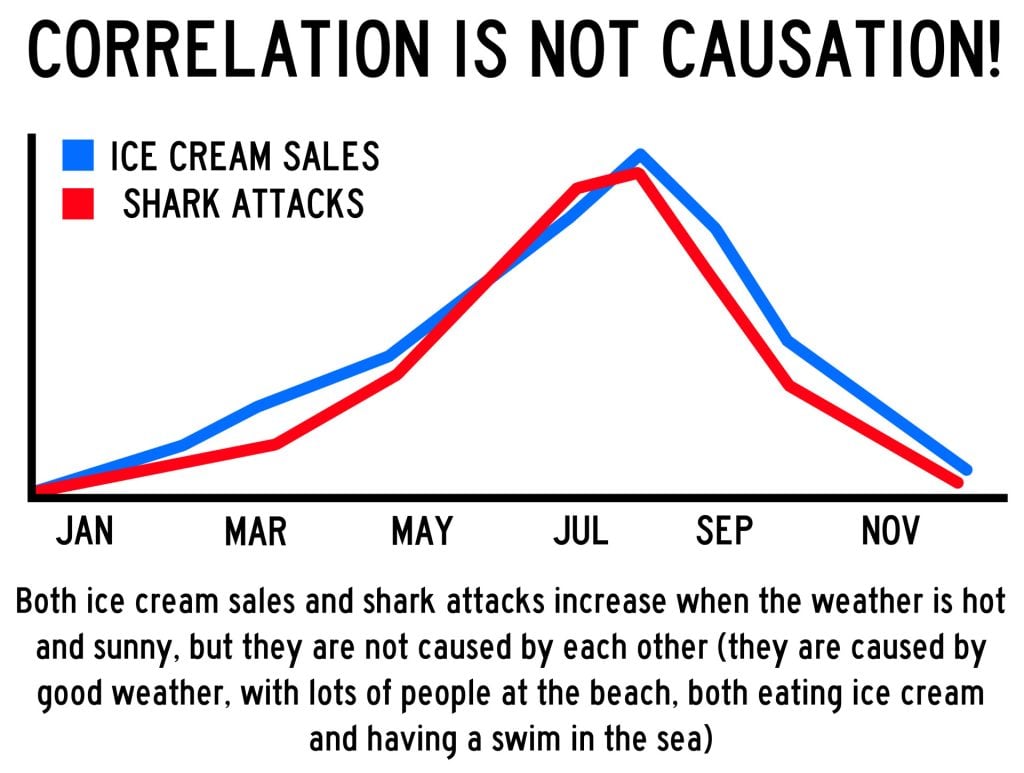
Interview Methods
Interviews are commonly divided into two types: structured and unstructured.
A fixed, predetermined set of questions is put to every participant in the same order and in the same way.
Responses are recorded on a questionnaire, and the researcher presets the order and wording of questions, and sometimes the range of alternative answers.
The interviewer stays within their role and maintains social distance from the interviewee.
There are no set questions, and the participant can raise whatever topics he/she feels are relevant and ask them in their own way. Questions are posed about participants’ answers to the subject
Unstructured interviews are most useful in qualitative research to analyze attitudes and values.
Though they rarely provide a valid basis for generalization, their main advantage is that they enable the researcher to probe social actors’ subjective point of view.
Questionnaire Method
Questionnaires can be thought of as a kind of written interview. They can be carried out face to face, by telephone, or post.
The choice of questions is important because of the need to avoid bias or ambiguity in the questions, ‘leading’ the respondent or causing offense.
- Open questions are designed to encourage a full, meaningful answer using the subject’s own knowledge and feelings. They provide insights into feelings, opinions, and understanding. Example: “How do you feel about that situation?”
- Closed questions can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no” or specific information, limiting the depth of response. They are useful for gathering specific facts or confirming details. Example: “Do you feel anxious in crowds?”
Its other practical advantages are that it is cheaper than face-to-face interviews and can be used to contact many respondents scattered over a wide area relatively quickly.
Observations
There are different types of observation methods :
- Covert observation is where the researcher doesn’t tell the participants they are being observed until after the study is complete. There could be ethical problems or deception and consent with this particular observation method.
- Overt observation is where a researcher tells the participants they are being observed and what they are being observed for.
- Controlled : behavior is observed under controlled laboratory conditions (e.g., Bandura’s Bobo doll study).
- Natural : Here, spontaneous behavior is recorded in a natural setting.
- Participant : Here, the observer has direct contact with the group of people they are observing. The researcher becomes a member of the group they are researching.
- Non-participant (aka “fly on the wall): The researcher does not have direct contact with the people being observed. The observation of participants’ behavior is from a distance
Pilot Study
A pilot study is a small scale preliminary study conducted in order to evaluate the feasibility of the key s teps in a future, full-scale project.
A pilot study is an initial run-through of the procedures to be used in an investigation; it involves selecting a few people and trying out the study on them. It is possible to save time, and in some cases, money, by identifying any flaws in the procedures designed by the researcher.
A pilot study can help the researcher spot any ambiguities (i.e. unusual things) or confusion in the information given to participants or problems with the task devised.
Sometimes the task is too hard, and the researcher may get a floor effect, because none of the participants can score at all or can complete the task – all performances are low.
The opposite effect is a ceiling effect, when the task is so easy that all achieve virtually full marks or top performances and are “hitting the ceiling”.
Research Design
In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time
Sometimes, we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time.
In cohort studies , the participants must share a common factor or characteristic such as age, demographic, or occupation. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study in which researchers monitor and observe a chosen population over an extended period.
Triangulation means using more than one research method to improve the study’s validity.
Reliability
Reliability is a measure of consistency, if a particular measurement is repeated and the same result is obtained then it is described as being reliable.
- Test-retest reliability : assessing the same person on two different occasions which shows the extent to which the test produces the same answers.
- Inter-observer reliability : the extent to which there is an agreement between two or more observers.
Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a systematic review that involves identifying an aim and then searching for research studies that have addressed similar aims/hypotheses.
This is done by looking through various databases, and then decisions are made about what studies are to be included/excluded.
Strengths: Increases the conclusions’ validity as they’re based on a wider range.
Weaknesses: Research designs in studies can vary, so they are not truly comparable.
Peer Review
A researcher submits an article to a journal. The choice of the journal may be determined by the journal’s audience or prestige.
The journal selects two or more appropriate experts (psychologists working in a similar field) to peer review the article without payment. The peer reviewers assess: the methods and designs used, originality of the findings, the validity of the original research findings and its content, structure and language.
Feedback from the reviewer determines whether the article is accepted. The article may be: Accepted as it is, accepted with revisions, sent back to the author to revise and re-submit or rejected without the possibility of submission.
The editor makes the final decision whether to accept or reject the research report based on the reviewers comments/ recommendations.
Peer review is important because it prevent faulty data from entering the public domain, it provides a way of checking the validity of findings and the quality of the methodology and is used to assess the research rating of university departments.
Peer reviews may be an ideal, whereas in practice there are lots of problems. For example, it slows publication down and may prevent unusual, new work being published. Some reviewers might use it as an opportunity to prevent competing researchers from publishing work.
Some people doubt whether peer review can really prevent the publication of fraudulent research.
The advent of the internet means that a lot of research and academic comment is being published without official peer reviews than before, though systems are evolving on the internet where everyone really has a chance to offer their opinions and police the quality of research.
Types of Data
- Quantitative data is numerical data e.g. reaction time or number of mistakes. It represents how much or how long, how many there are of something. A tally of behavioral categories and closed questions in a questionnaire collect quantitative data.
- Qualitative data is virtually any type of information that can be observed and recorded that is not numerical in nature and can be in the form of written or verbal communication. Open questions in questionnaires and accounts from observational studies collect qualitative data.
- Primary data is first-hand data collected for the purpose of the investigation.
- Secondary data is information that has been collected by someone other than the person who is conducting the research e.g. taken from journals, books or articles.
Validity means how well a piece of research actually measures what it sets out to, or how well it reflects the reality it claims to represent.
Validity is whether the observed effect is genuine and represents what is actually out there in the world.
- Concurrent validity is the extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure and obtains close results. For example, a new intelligence test compared to an established test.
- Face validity : does the test measure what it’s supposed to measure ‘on the face of it’. This is done by ‘eyeballing’ the measuring or by passing it to an expert to check.
- Ecological validit y is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other settings / real life.
- Temporal validity is the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalized to other historical times.
Features of Science
- Paradigm – A set of shared assumptions and agreed methods within a scientific discipline.
- Paradigm shift – The result of the scientific revolution: a significant change in the dominant unifying theory within a scientific discipline.
- Objectivity – When all sources of personal bias are minimised so not to distort or influence the research process.
- Empirical method – Scientific approaches that are based on the gathering of evidence through direct observation and experience.
- Replicability – The extent to which scientific procedures and findings can be repeated by other researchers.
- Falsifiability – The principle that a theory cannot be considered scientific unless it admits the possibility of being proved untrue.
Statistical Testing
A significant result is one where there is a low probability that chance factors were responsible for any observed difference, correlation, or association in the variables tested.
If our test is significant, we can reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative hypothesis.
If our test is not significant, we can accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative hypothesis. A null hypothesis is a statement of no effect.
In Psychology, we use p < 0.05 (as it strikes a balance between making a type I and II error) but p < 0.01 is used in tests that could cause harm like introducing a new drug.
A type I error is when the null hypothesis is rejected when it should have been accepted (happens when a lenient significance level is used, an error of optimism).
A type II error is when the null hypothesis is accepted when it should have been rejected (happens when a stringent significance level is used, an error of pessimism).
Ethical Issues
- Informed consent is when participants are able to make an informed judgment about whether to take part. It causes them to guess the aims of the study and change their behavior.
- To deal with it, we can gain presumptive consent or ask them to formally indicate their agreement to participate but it may invalidate the purpose of the study and it is not guaranteed that the participants would understand.
- Deception should only be used when it is approved by an ethics committee, as it involves deliberately misleading or withholding information. Participants should be fully debriefed after the study but debriefing can’t turn the clock back.
- All participants should be informed at the beginning that they have the right to withdraw if they ever feel distressed or uncomfortable.
- It causes bias as the ones that stayed are obedient and some may not withdraw as they may have been given incentives or feel like they’re spoiling the study. Researchers can offer the right to withdraw data after participation.
- Participants should all have protection from harm . The researcher should avoid risks greater than those experienced in everyday life and they should stop the study if any harm is suspected. However, the harm may not be apparent at the time of the study.
- Confidentiality concerns the communication of personal information. The researchers should not record any names but use numbers or false names though it may not be possible as it is sometimes possible to work out who the researchers were.
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

A-Level Psychology
A-level Psychology AQA Revision Notes

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This guide provides an overview of research methods, how to choose and use them, and supports and resources at UC Berkeley. As Patten and Newhart note in the book Understanding Research Methods , "Research methods are the building blocks of the scientific enterprise.
The Beginner's Guide to Statistical Analysis | 5 Steps & Examples. Statistical analysis means investigating trends, patterns, and relationships using quantitative data. It is an important research tool used by scientists, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
data analysis, the process of systematically collecting, cleaning, transforming, describing, modeling, and interpreting data, generally employing statistical techniques. Data analysis is an important part of both scientific research and business, where demand has grown in recent years for data-driven decision making.
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
Volume 19, Issue 1. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484320903890. Contents. PDF / ePub. Abstract. Given the vast and diverse qualitative analytic landscape, what might be a generative starting point for researchers who desire to learn how to produce quality qualitative analyses?
Meta-analysis is the quantitative, scientific synthesis of research results. Since the term and modern approaches to research synthesis were first introduced in the 1970s, meta-analysis...
Browse the latest on research analysis from the world's leading research journal.
Research is the process of finding information, while analysis is the process of evaluating and interpreting that information to make informed decisions. Analysis is a critical step in the decision-making process, providing context and insights to support informed choices.
Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement.
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1, 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3, 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and...
Introduction. Statistical analysis is necessary for any research project seeking to make quantitative conclusions. The following is a primer for research-based statistical analysis. It is intended to be a high-level overview of appropriate statistical testing, while not diving too deep into any specific methodology.
Definition: Data analysis refers to the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, drawing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to interpret and derive insights from large datasets.
Definition of research in data analysis: According to LeCompte and Schensul, research data analysis is a process used by researchers to reduce data to a story and interpret it to derive insights. The data analysis process helps reduce a large chunk of data into smaller fragments, which makes sense.
Table of Contents. What is Research? Types of Research Methods. Research Process: How To Conduct Research. Top 10 Best Practices for Conducting Research in 2023. What is Research? Research is defined as a meticulous and systematic inquiry process designed to explore and unravel specific subjects or issues with precision.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research and your dissertation topic.
Research methods in psychology are systematic procedures used to observe, describe, predict, and explain behavior and mental processes. They include experiments, surveys, case studies, and naturalistic observations, ensuring data collection is objective and reliable to understand and explain psychological phenomena.
Concept analysis is a useful qualitative research method for psychologists aiming to define, clarify or critique concept meaning and use in theory, practice or research. This article explains Reformative Concept Analysis (RCA), a novel method derived from nursing and political science concept analysis approaches, and reformed for applied ...
Market research analysis is a vital tool that helps businesses gather and interpret data to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, identify opportunities for growth, and stay competitive in their respective markets.